This explains why annuity amounts (cash flows) can be referred to as deposits and payments at the same time. An annuity is defined as a series of equal cash amounts (cash flows, payments, deposits, etc). For example, if I were to promise to pay you $100 per year for the next 3 years, that arrangement could be considered to be an annuity. What’s more, you can analyze the result by following the progress of balances in the dynamic chart or the annuity table. For example, you can use it either for regular deposits or withdrawals, for multiple frequencies, or you can compare ordinary annuity vs. annuity due.
Learn About Top Annuity Products & Get a Free Quote
Investors who cannot take on this risk are probably better off with a fixed annuity. Keep in mind that variable annuities have some of the highest fees in the financial industry. Rider Charges–An annuity rider is an amendment to an annuity contract that has the effect of either expanding or restricting the policy’s benefits or excluding certain conditions from coverage. A popular example is an income rider; in the case of dramatic drops in the value of mutual fund investments in an annuity, an income rider prevents it from falling below a guaranteed amount. Another common rider is an annual increase rider that increases payment each year by a predetermined percent, usually 1% to 5%, in order to keep pace with inflation. Other examples include a long-term care rider that covers nursing home costs or a legacy through a guaranteed death benefit.
Retiring as an Educator: A Professor’s Tips for Supplementing Savings
- The advantage of a deferred annuity, as compared to an immediate annuity, is that taxes on built capital are deferred.
- If you want to figure out what the annuity might be worth over the course of ten years, use “10” in place of “n” in the formula above.
- This small change will result in a slightly higher future value compared to the Ordinary Annuity, reflecting the additional compounding period for each payment.
- We may also, at times, sell lead data to partners in our network in order to best connect consumers to the information they request.
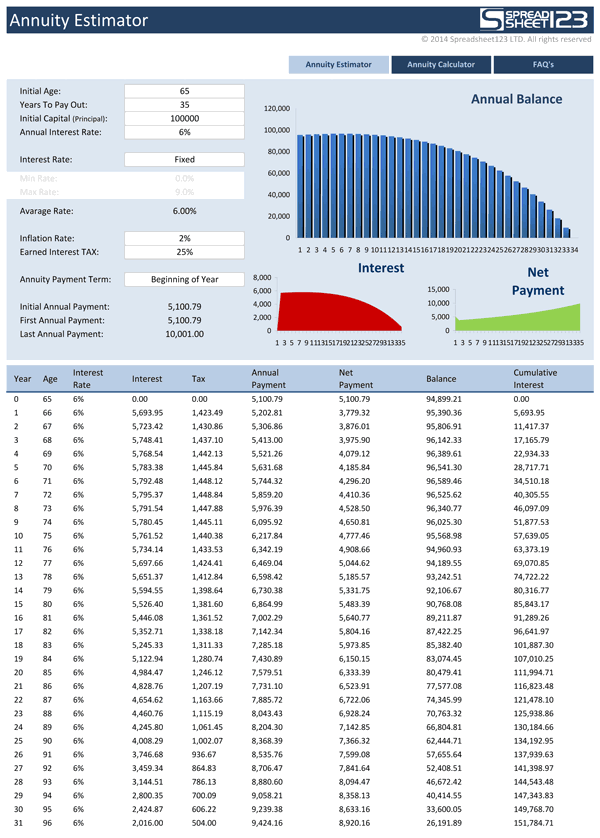
- Use our annuity calculator to calculate the future value, present value, or payout of an annuity.
Payments from this type of annuity are postponed and are dependent on market conditions so may fluctuate. Whether the fees are bundled upfront or will be applied over time will depend on the policies of the company issuing the annuity. You should read the fine print on any contract for an underwritten or direct sold annuity. Use this calculator to find the future value of annuities due, ordinary regular annuities and growing annuities. If the winner was to invest all of his lottery prize money, he would have [latex]\$2,544,543.22[/latex] after [latex]25[/latex] years.

What kind of annuities are best for the seniors?
The advanced payments immediately affect the future value of the annuity as the money stays in your bank for longer and, therefore, earns interest for one additional period. Therefore, with the annuity due, the future value of the annuity is higher than with the ordinary annuity. The purpose of this calculator is to compute the future value of a series of deposits. This is an investment or saving account and, you are calculating the accumulation of a series of deposits, the annuity payments, and what the total value will be at some time in the future. But even this simple example, which did not require an interest conversion, is cumbersome, and time-consuming, to solve using the formula.
How do annuities work?
A financial calculator can quickly solve annuity problems, with the added bonus of not requiring an interest conversion in situations where the payment frequency and compounding frequency are not equal. For example, this formula may be used to calculate how much money will be in a savings account at a given point in time given a specified interest rate. The effects of compound interest—with compounding periods ranging from daily to annually—may also be included in the formula.
Quick Pros and Cons of Annuities
You should consider the annuity calculator as a model for financial approximation. All payment figures, balances, and interest figures are estimates based on the data you provided in the specifications that are, despite our best effort, not exhaustive. Knowing how to correctly calculate annuity returns can help you make better financial decisions and understand if investing in an annuity is right for you. Here are some key benefits and helpful tips to make the most of our annuities calculator. These annuities also offer an immediate stream of income; however, the payments will be based on changing market conditions, and your annual payment may increase or decrease over time. These annuities involve making a large lump sum payment and immediately gaining access to an annual payout for the rest of your life.
The biggest limitation of the fixed annuity calculator is that it cannot predict how a fixed annuity’s interest rate might change over the contract’s term. The initial interest rate of a fixed annuity is usually only guaranteed for the first year or first few years of the contract. That is how much interest earnings you will be giving up by paying for the data plan for the next 30-years (of course, your loss will be the data plan company’s gain).
However, in practice and in everyday life annuity meaning takes a more explicit form. Buying an annuity usually refers to investment plans, for example insurance products, that provide a steady stream of income in retirement. For example, you can buy an annuity that requires a single upfront payment, or a series of payments to the insurance company. Then, the insurance company pays you either one lump-sum or multiple payments if the insurance pays out. Our online tools will provide quick answers to your calculation and conversion needs.
Determining the future value of an annuity is critical when deciding whether to invest. In this guide, we will discuss how to calculate the future value of several of today’s most common types of annuities. On this page, we can solve for any one of these four variables, viz., FVA, P, i and n. Unlike spreadsheets and fees deduction and financial calculators, there is no convention of negative numbers in our future value of annuity calculator and only positive values must be entered. Annuities are taxable, however, the growth of the annuity is tax-deferred so you won’t pay any taxes on your annuity until you begin receiving payments.
Understanding annuities (and other Time Value of Money principles) is critical to that process. And that’s only considering just one of the possible hundreds of the non-essential expenditures you likely make on a regular basis. Continuing with our example, if I agreed to make the $100 annual payments at the beginning of each year, our arrangement would be considered to be an annuity due.

